It is a lever you grab repeatedly while shifting gears. You also know that it disengages the power going from the engine towards the rear wheel when you pull it in. But do you know how a typical motorcycle clutch works? And how you can inculcate a few good riding habits to make it last longer? Well, let’s begin with the part which will acquaint you with the functionality of a motorcycle engine’s clutch.
Know More
How Does It Work?
The basic job of the clutch is to temporarily disconnect the engine from the transmission and drivetrain system which drives the rear wheel. Unless that happens, it is nearly impossible to mate an idling engine with the transmission and move a geared motorcycle, which is at a standstill, forwards. It is possible to shift gears without the clutch when the bike is moving, but the result isn’t always smooth and if performed incorrectly, the grinding can even damage the gearbox for good.
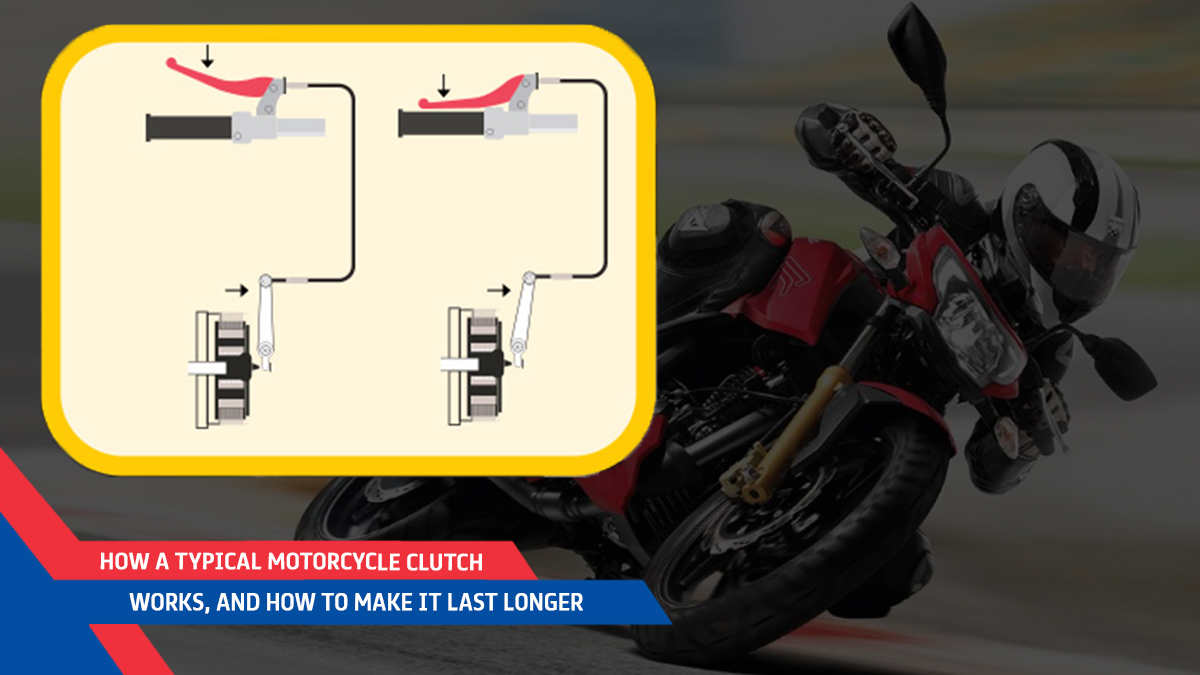
The lever which is pulled by your left hand is connected to a circular clutch assembly, which sits closer to the engine, via a cable or a hydraulic system. The assembly consists of a pressure plate on the outermost side which faces the engine cover. As the name suggests, with the help of springs which are bolted on the outside, the pressure plate acts like a lid which pushes in and pulls out to compress and decompress the “Clutch Pack“. This pack consists of a series of friction and steel plates which are placed alternately and have teeth around their outer and inner circumference respectively.
These plates are closely stacked together, where the teeth of the friction plates interlock with the slots grooves on an outer basket covering the width of the entire assembly. The steel plates which are placed between the friction plates interlock against the grooves on a smaller inner hub, which has a smaller diameter than the outer basket and is placed inside, adjacent to it.
The outer basket is lined with toothy gears along its circumference, which is connected to and driven by the engine’s crankshaft. The inner hub is splined on the transmission’s input shaft and rotates along with it. When the clutch lever is out, the fully compressed springs on the pressure plate sandwich everything together. As the steel and friction plates are pressing against each other at this time, the rotation of the friction disc results in rotation of the steel disc and vice-versa. As a result, power is transferred from the engine to the transmission.
When you pull the clutch lever in, the action causes the compressed springs on the pressure plate to retract. As a result, the friction and steel plates which are forced together separate and begin to rotate independently, disconnecting the engine from the transmission system. If you’ve ever experienced that the clutch lever is hard to pull in on some motorcycles, it is because the pressure acting on the external plate is increased to enhance the clutch’s ability to handle engine power. It is one of the alternatives to using a smaller clutch assembly with many plates or a larger assembly with fewer plates.
There are two main designs of motorcycle clutch assemblies – A wet clutch and a dry clutch. A wet clutch is bathed in the engine oil, as it provides cooling and lubricates the various interlocking components of the assembly. It has a longer life and can withstand harsh conditions better, in comparison to a dry system. A dry clutch as the name suggests doesn’t require an oil bath. The upside to that? It doesn’t contaminate the engine oil with particles which are a part of normal wear and tear of the clutch system. The other advantage is that since it doesn’t spin through an oil bath which also lubricates the engine, there is lesser drag and the system doesn’t rob the engine’s power.
How to ensure longevity for your motorcycle clutch?
There are some basics which you can follow to enhance the life of a clutch assembly. Since most bikes these days employ a wet clutch, ensure that the engine oil is replaced on time. Avoid riding the clutch, where some of your fingers rest on the lever when you ride and you’re accidentally pulling the clutch in, all throughout.
If you like indulging in acts like pulling wheelies or performing burnouts, the life of your clutch will reduce almost by half or even less. Aggressive downshifting and releasing the clutch abruptly will round off the teeth on those clutch plates and the grooves on the inner hub and outer basket. If you begin to experience slippage, get the clutch assembly checked and replace any components which could cause further damage. Be smooth with your inputs as much as you can and that’s the best you can do to make that clutch assembly last long, really long.

I have Tvs tricicle, its not faster. Is it housing problem ?